Zero Trust Lines of Defenses: Mapping the NIST Zero Trust Architecture Report
Zero Trust Lines of Defense Mapping the NIST Zero Trust Architecture Report “Trust is a vulnerability that cyber threats exploit. Zero Trust is how we
A modern and agile defense paradigm
For those who are responsible for the management of a company’s IT infrastructure, it is quite clear that the moat technique, i.e. the old idea of building a moat around a castle to keep intruders out, is no longer relevant. This is not only inefficient but also hardly feasible given the number and diversity of entry points into the IT environment.
The risks organizations face aren’t just from external attackers, they also come from insiders, whether through accidental errors, compromised credentials, or intentional wrongdoing. Relying solely on perimeter defenses creates blind spots, leaving organizations vulnerable to threats that originate from within.
Simply verifying a person or device before granting access to company resources is no longer enough. Cloud adoption, remote work, and third-party integrations have blurred network boundaries. Moreover, if an attacker gains control of a legitimate identity, they can move freely through the system without raising alarms.
With businesses increasingly depending on public, private, and hybrid cloud services, a crucial question arises: How can you ensure trust is continuously maintained?
A Zero Trust approach, has proven to be more effective. It is based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security methods that assume users inside the network are safe, Zero Trust ensures continuous authentication, strict access controls, and constant monitoring.
Key principles include:
Implementing Zero Trust security offers significant benefits in terms of protection, compliance, and operational efficiency:
cyberelements offers a Zero Trust access management solution designed to secure modern IT and OT environments. With cyberelements, organizations benefit from:
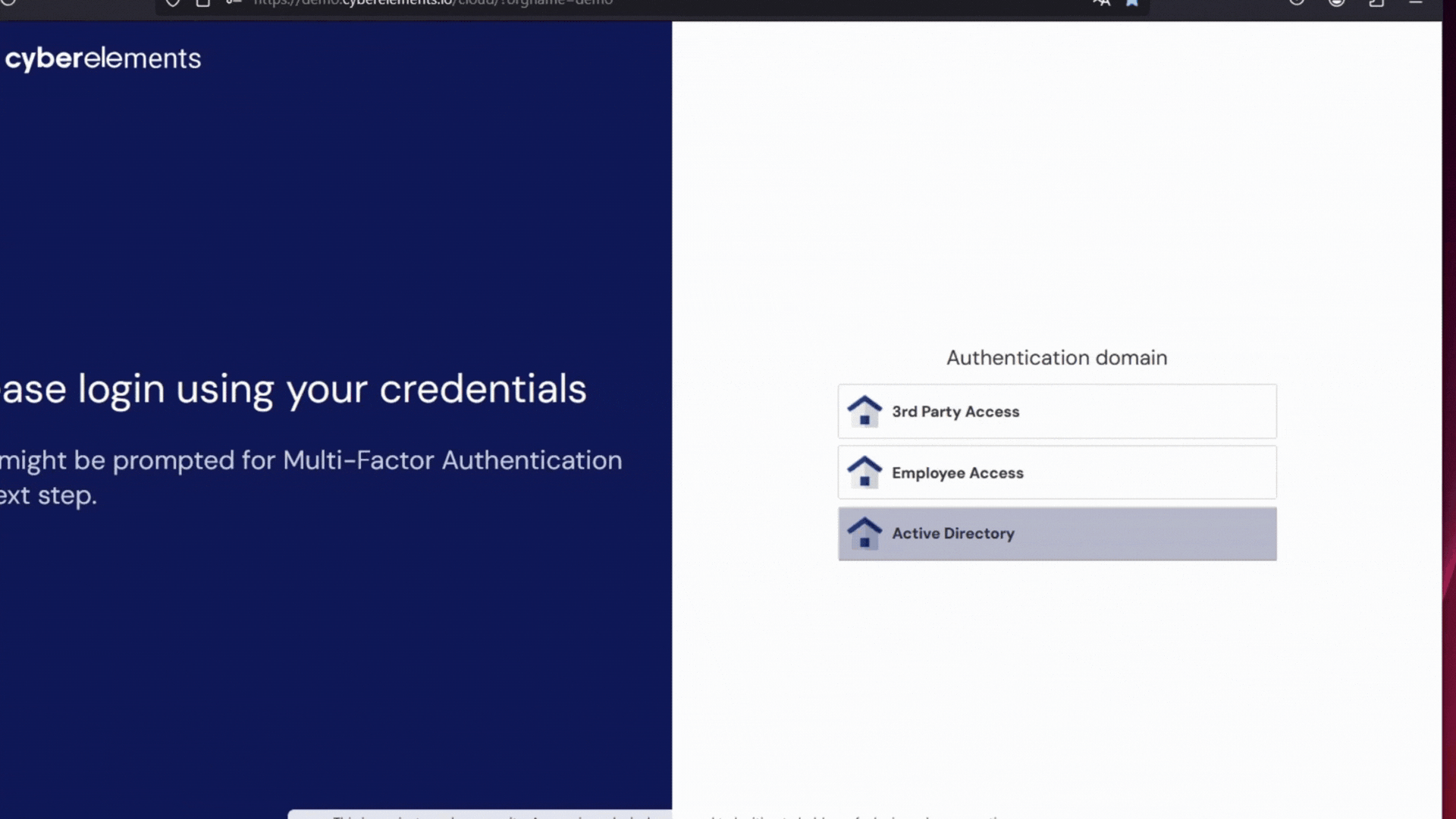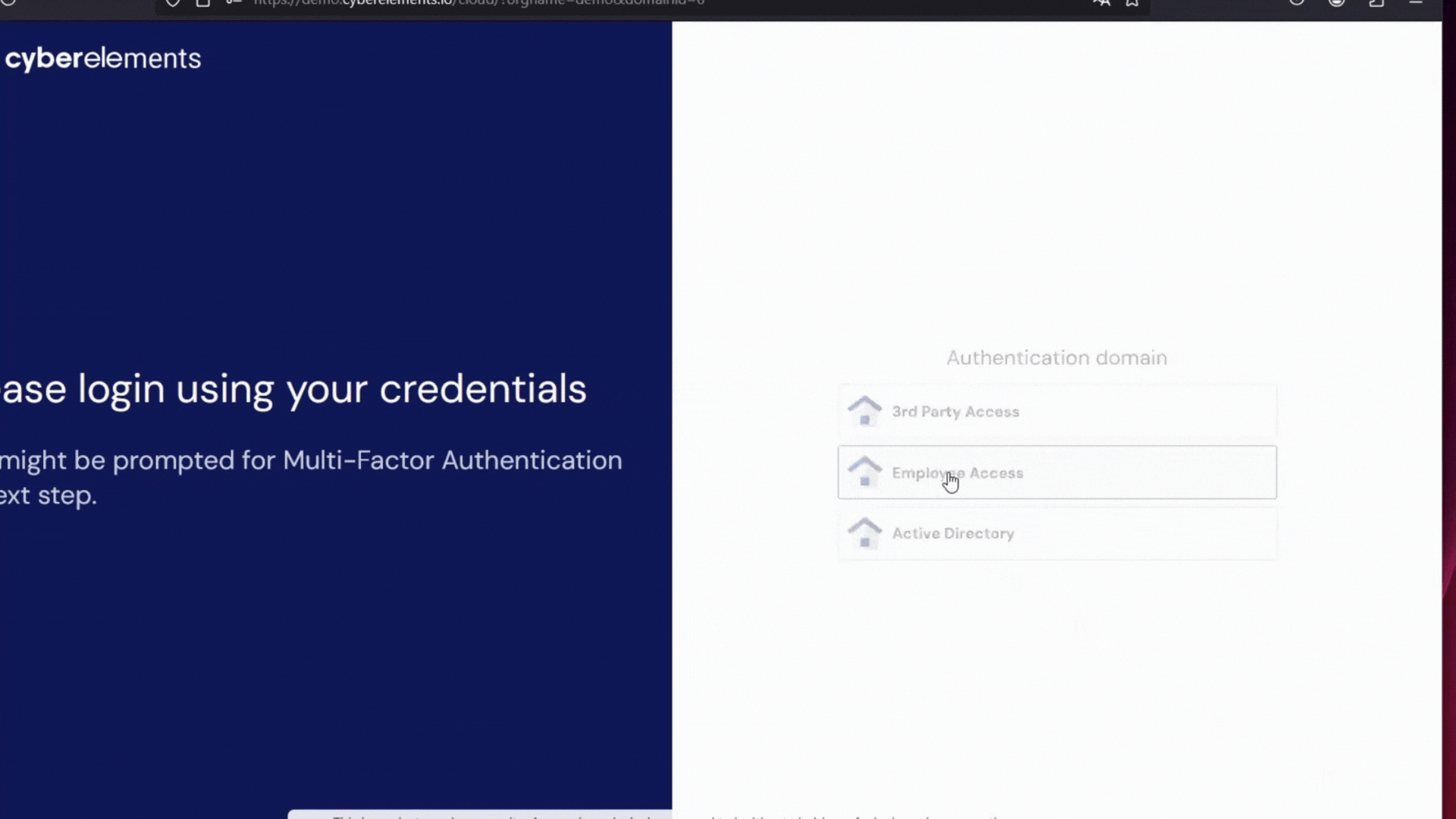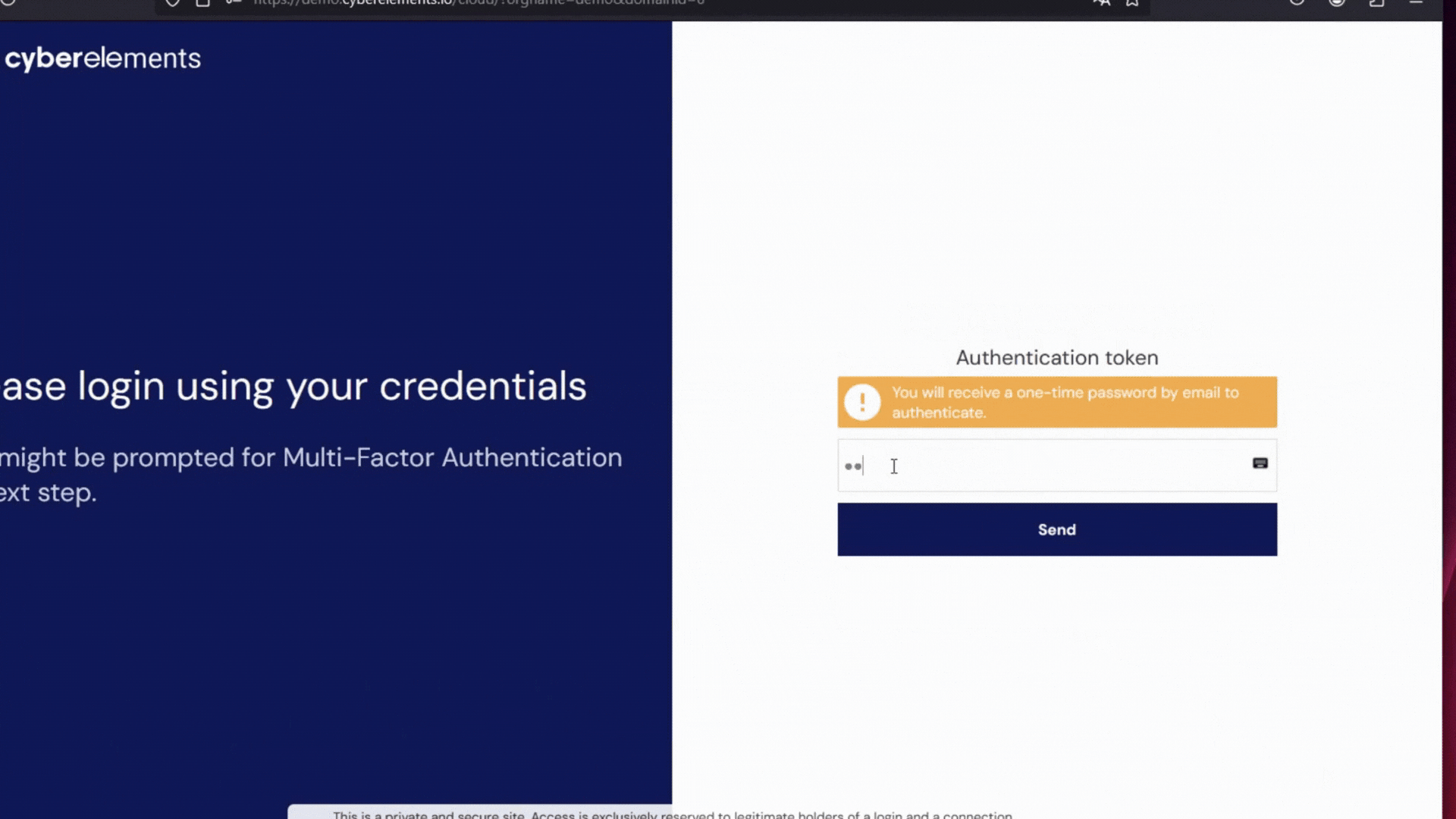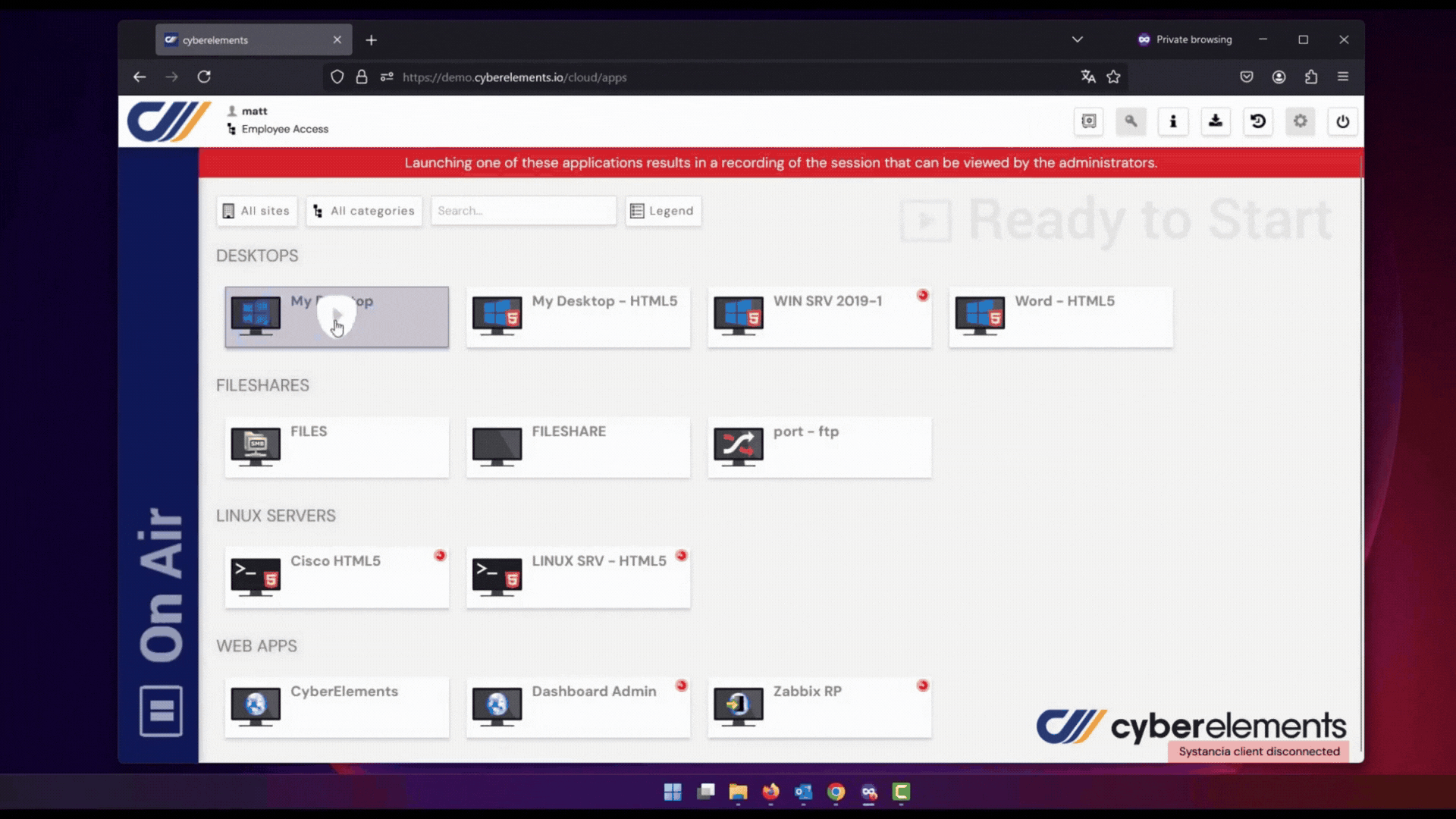
cyberelements shifts your cybersecurity strategy by moving away from direct access models. Instead, it provides a double barrier architecture based on a Mediation and a Gateway. Instead of exposing internal resources, a secure intermediary manages access requests and only grants entry under strict verification.
The mediation server, typically placed in a demilitarized zone (DMZ), acts as a checkpoint by:
By using the cyberelements approach, businesses significantly reduce their attack surface, ensuring that only legitimate users can interact with corporate data and applications.
Zero Trust Lines of Defense Mapping the NIST Zero Trust Architecture Report “Trust is a vulnerability that cyber threats exploit. Zero Trust is how we