What is Native Zero Trust Remote PAM?
What is Native Zero Trust Remote PAM? By the year 2026, organizations embracing least privilege approaches to RPAM use cases are projected to significantly reduce
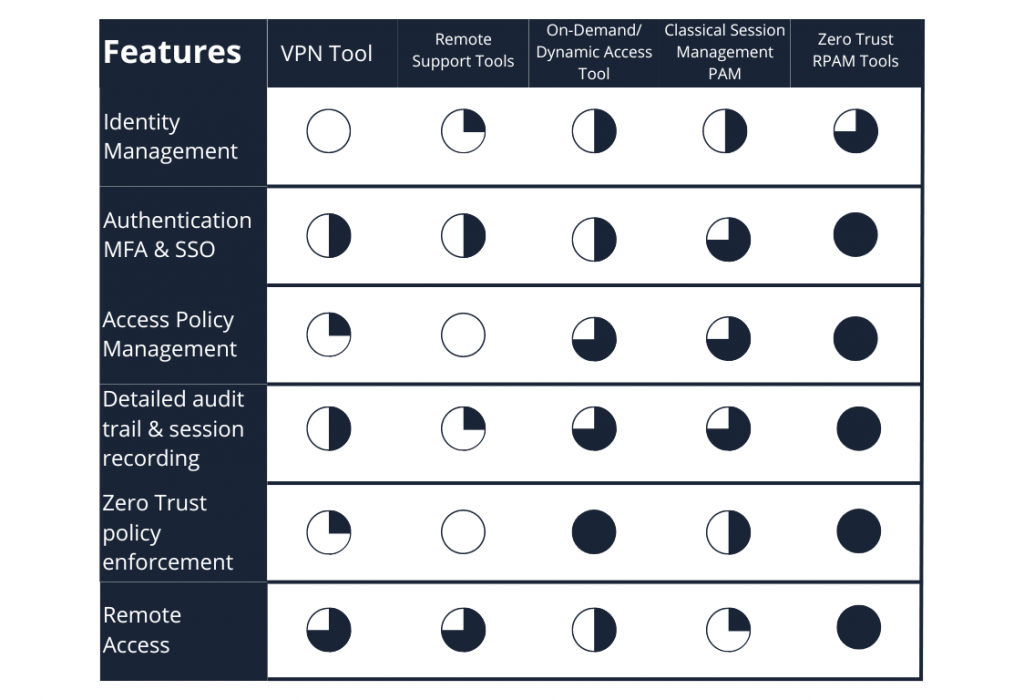
Which tools should you choose?
Although remote maintenance is essential for ensuring organizational efficiency it comes with cybersecurity risks related to remote access. These risks can be mitigated or even eliminated with the right IT solutions. Various tools are commonly used for remote maintenance, including remote control software, VPNs, ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access), and PAM (Privileged Access Management). However, not all of these solutions offer the same level of cybersecurity.
Remote maintenance is designed to resolve IT issues or carry out operations by remotely accessing a system or network. It enhances responsiveness and convenience, ensuring seamless business continuity. It includes:
This second scenario poses the greatest security risks to the information system. When a service provider remotely controls a system, several challenges must be addressed :
While remote control software is well-suited for internal helpdesk tasks (organization’s IT department and employees), it lacks the necessary security features for remote access by service providers performing system maintenance.
In this scenario, an agent must be installed to enable external access. However, this agent can be detected by tools that scan for open ports, making it a potential entry point for hackers.
A service provider accessing remotely a device, is granted full access rights. However, their permissions should be restricted based on their specific role to minimize security risks and prevent lateral movement.
Remote desktop solutions do not offer enhanced authentication to strengthen security. Additionally, traceability is limited to basic log records stored only on the workstation itself, providing insufficient oversight.
VPNs, commonly used by organizations to grant remote access to service providers, do not fully meet all security requirements. Originally, VPNs were designed to connect two trusted networks within the same organization.
From the organization’s perspective, the service provider cannot be considered fully trustworthy, as there is no control over their network.
VPNs do not support the implementation of the principle of least privilege, a critical requirement for securing IT systems.
Like remote control software, VPNs require agent installation. These agents must be regularly updated to patch vulnerabilities. However, since it typically takes a month on average for a vendor to release a patch and another month for an organization to deploy it across all agents, the system remains exposed to these vulnerabilities for a long period.
For remote maintenance by external service providers, ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) is the recommended solution, as its security features are specifically designed for remote access from untrusted devices.
cyberelements, as a zero-trust secure remote access solution, provides:
cyberelements restricts external service providers’ rights and permissions to the necessary applications.
The accessed resources are “hidden” from the Internet. The connection to the resource is made through an internal gateway, meaning the resource is not exposed to the Internet. It is isolated from the Internet while still accessible via the ZTNA solution. Access to resources is granted only when needed and used, through temporary and random ports.
cyberelements provides detailed traceability, allowing you to know who connected to what.
By defining your own security measures, the integrity of each device is checked before granting access to applications and systems.
Strong Authentication
cyberelements allows strong authentication, supporting a range of solutions, and offering Single Sign-On (SSO) for backend resources.
PAM solutions provide full control and monitoring capabilities, real-time analysis, and access activity logs (allowing the organization to track who connected to what and for what purpose).
cyberelements, the Zero Trust Remote Privileged Access Management solution, allowing:
By applying Zero Trust principles, cyberelements enables organizations to implement the principle of least privilege, based on the assumption that all users and privileged endpoints are potential security threats. cyberelements, the Zero Trust Remote PAM solution, is designed to secure privileged access, particularly that of external service providers.
What is Native Zero Trust Remote PAM? By the year 2026, organizations embracing least privilege approaches to RPAM use cases are projected to significantly reduce
With the rise of remote work and the increasing threat of cyberattacks, it’s never been more critical to ensure that your organization’s critical resources are protected.